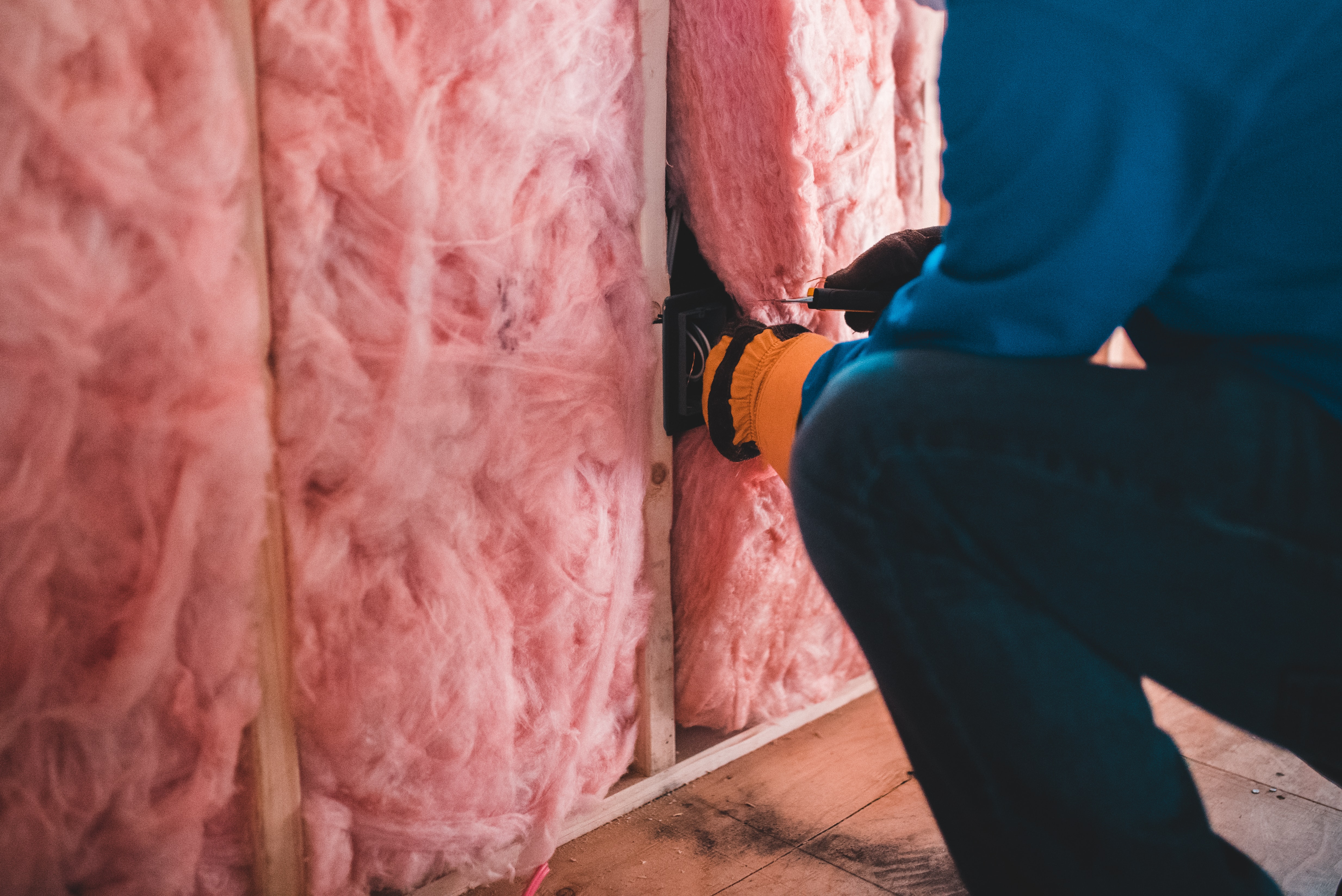

Insulation is one of the fundamental elements in keeping buildings comfortable, healthy, and efficient.
You may associate insulation just with maintaining a building’s temperature, but it serves a much larger role in the building envelope. Effective insulation can lower energy bills, stop mold growth, help dampen sound, and more.
In this article, we’ll cover: what insulation is, how it works, and how it relates to R-Values.
What is Insulation – That Pink Stuff?
Insulation refers to materials with insulating properties that are used to fill empty spaces, such as behind walls, between floors, in attics, etc.
There are several types of insulation, including blanket insulation aka “that pink stuff”. Each type of insulation is created with different materials, have different applications, installation methods, and advantages.
How Insulation Works
To put it simply, insulation keeps buildings comfortable by limiting the amount of heat that enters, moves around, and exits a building.
To get a better understanding of how insulation works, you should know about the three types of heat flow:
- Radiation – heat that travels in a straight line and heats anything solid in its path. An example of radiant heat would be a fireplace.
- Conduction – heat that moves through materials. An example of conduction heat would be when the handle of a frying pan gets hot when the pan is over flames.
- Convection – how heat circulates through liquid and gases. An example of convection heating would be a radiator, which draws cool air from the bottom and outputs warn air from the top.
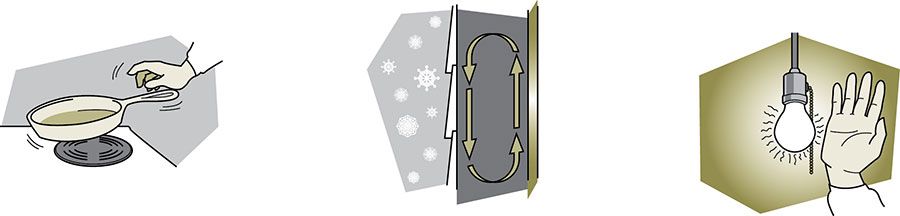
Image from NRCAN.gc.ca
Most insulation materials work by slowing conduction and convection heat flow.
Heat naturally flows to the cooler areas around it until there is no difference in temperature. When it is winter, heat is drawn to attics, basements, and the outdoors. When it is summer, the heat from the outdoors is drawn inside. Effective insulation provides a strong resistance to heat flow and limits how much a furnace/air conditioner is needed to maintain heat levels.
For a more detailed breakdown of how insulation works, check out the below video.
How is the Effectiveness of Insulation Measured?
Insulation’s resistance to heat flow is determined by its thermal resistance or R-Value. The higher the R-Value, the most effective the insulation is. For example, one of our most strongly insulated SIS Panels™ is our Magnesium Oxide (MgO) SIS Panel with a Phenolic core. It has an R-Value of R17.72 with 2” foam and an R-Value of R26.22 with 3” foam.

Insulation’s resistance to heat flow is determined by its thermal resistance or R-Value. The higher the R-Value, the most effective the insulation is. For example, one of our most strongly insulated SIS Panels™ is our Magnesium Oxide (MgO) SIS Panel with a Phenolic core. It has an R-Value of R17.72 with 2” foam and an R-Value of R26.22 with 3” foam.
There are many factors that affect R-Values, such as: where the insulation is being installed, if there is multilayered insulation, how thick the insulation is, the climate where the insulation is being installed, and more.
High-quality insulation can make a building more comfortable, healthy, and efficient. Homeowners may not give it much thought, but it is an important part of every building.
Want a more in depth understanding of insulation? Check out the sources we used to build this article.
https://www.energy.gov/energysaver/insulation
https://globalnews.ca/news/1776037/what-you-need-to-know-about-home-insulation/
https://blog.chba.ca/2019/04/18/the-science-behind-a-net-zero-home/
